
An Introduction to Emission Inventories
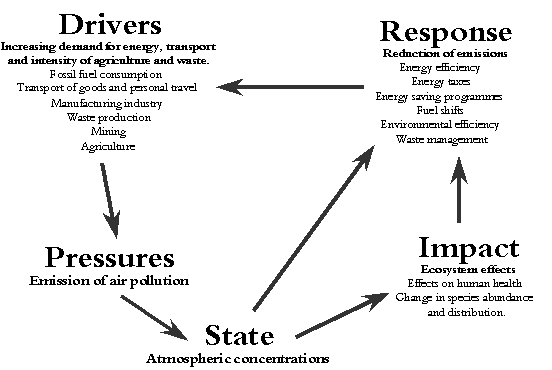
Emission inventories play an important role in assessing the effects of anthropogenic (man-made) activity on atmospheric pollution. The principal human demands for energy, transportation, materials and food may be regarded as the "drivers" for the production of air pollutants. In order for an economy to continue to develop in a sustainable way these sources of pollution must be managed. To do this we must understand the "impacts"- i.e. what types of pollution affect which parts of the environment or human health, and to what extent. To decide whether action is necessary we also need to know the "state" of the environment- i.e. to evaluate whether the levels in the environment exceed those which will cause environmental harm.
In taking appropriate action we must be able to respond in a focused way to control and reduce pollution while avoiding larger-scale damage to economic development. Emission inventories provide policy makers and the public with an understanding of the key polluting sources or the "pressures", how these sources have developed with economic growth and how they are likely to contribute to pollution in the future. This understanding is essential for a focused "response" to the problems associated with air pollution and to meet the demands of sustainable development.
Figure 1.1 shows how our understanding of the pressures (through emission inventories) interact with other areas of environmental knowledge such as impact assessment and monitoring (state). Figure 1.1 also clearly shows the relationship between: emission inventories, economic activity and effective environmental policy.
Figure 1.1 "DPSIR" Relational Diagram
